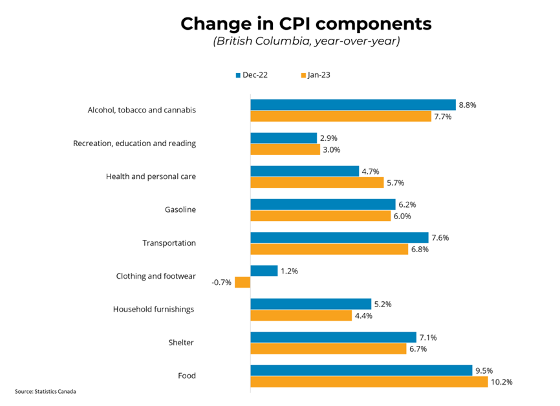
Canadian prices, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), rose 6.3 per cent on a year-over-year basis in December, a decrease from the 6.8 per cent rate in November. Falling gasoline (-13.1 per cent month on month) and fuel oil prices drove the decline, while softening costs for durable goods such as furniture and used vehicles also slowed price appreciation. Rising interest rates contributed to an increase in mortgage interest costs, which were up 18 per cent year-over-year as Canadians renewed or initiated higher-rate mortgages. In contrast, the Homeowner's Replacement Cost, which tracks home prices, continued to slow, pushing the CPI downwards. Month-over-month, on a seasonally-adjusted basis, prices were down 0.1 per cent in December. In BC, consumer prices rose 6.6 per cent year-over-year, down from 7.2 per cent last month.
While sharply declining gasoline prices were mostly responsible for the drop in CPI in December, there are encouraging signs that price appreciation is slowing in other sectors of the economy as well. Prices for household furnishings and equipment fell from last month amid ameliorating supply chain issues. The Bank of Canada's measures of core inflation, which strip out volatile components, ticked down in December for the first time since the summer. Weighing CPI numbers against a strong December jobs report, most analysts are expecting a final modest increase in rates on January 25th before the Bank concludes the tightening cycle.

Link: https://mailchi.mp/bcrea/canadian-inflation-december-2022
For more information, please contact: Gino Pezzani.
Comments:
Post Your Comment: